What is a Fork?
Definition
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are powered by decentralized, open-source software called blockchain. A fork occurs whenever a community makes changes to the blockchain’s protocol or basic rules.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are supported by decentralized, open software that anyone can participate in, known as blockchain. They are called blockchains because they are essentially made up of blocks of data, like a very long train, tracing back to the first transaction on the network. And because they are open-source, they rely on the community to maintain and develop their underlying code.
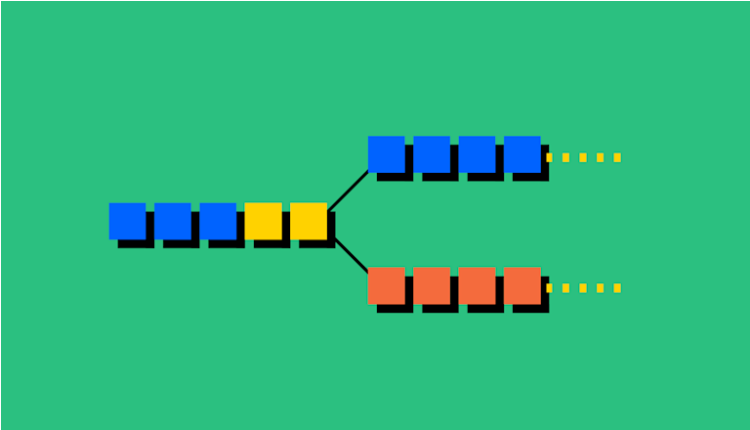
A fork occurs whenever the community makes changes to the blockchain’s protocol or basic rules. When this happens, the chain splits, creating a second blockchain that shares all the history with the original but moves in a new direction.
Why is this important?
Most digital currencies have independent development teams responsible for changes and improvements to the network, much like how changes to internet protocols continuously enhance web browsing. As a result, forks sometimes occur to make cryptocurrencies more secure or to add additional features.
However, developers of new cryptocurrencies may also use forks to create entirely new currencies and ecosystems.
Soft Fork: Think of a soft fork as a software upgrade for the blockchain. As long as it is adopted by all users, it becomes the new standard for the currency. Soft forks have been used to introduce new characteristics or functionalities to Bitcoin and Ethereum, typically at the programming level. Since the end result is a single blockchain, these changes are backward-compatible with previous forked blocks.
Hard Fork: A hard fork occurs when the code changes so much that the new version is no longer backward-compatible with earlier blocks. In this case, the blockchain splits into two: the original blockchain and a new version that follows a new set of rules. This creates an entirely new cryptocurrency, which is the origin of many well-known currencies. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Gold evolved from the original Bitcoin blockchain through hard forks.
Why do forks happen?
Just like all software requires upgrades, blockchains are updated for various reasons:
Adding functionalities
Addressing security risks
Resolving disagreements within the community about the direction of the cryptocurrency
How will forks continue to change the cryptocurrency landscape?
The Ethereum blockchain is designed to run "smart contracts," which are blocks of code that automatically execute a predetermined set of actions when specific conditions are met. Smart contract applications include everything from games and logistics tools to DeFi dapps.
As the platform running all these applications, you can think of the Ethereum blockchain as similar to an operating system for a computer. By this analogy, various Ethereum forks (Ethereum, Ethereum Classic, Ethereum 2.0) are like updated versions of the operating system, adding features or efficiencies that previous versions may have lacked.
Older forks can continue as stable platforms that validate maturity, while new forks can provide developers with entirely new ways to interact. (Old and new versions may eventually merge or continue to develop separately.)
Think of soft forks as "software upgrades" (like a phone requiring an update to the latest OS) and hard forks as entirely new operating systems (like Linux and Mac OS, both of which evolved from the UNIX platform fifty years ago).
















